Lung ultrasound is invaluable in the detection and diagnosis of lung consolidations. We describe how to master this ultrasound technique and integrate its findings into your clinical practice.

SHARE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Lung consolidation occurs when healthy lung tissue is replaced by substances such as pus, blood, fluid, or tissue, leading to swelling of the normal lung tissues. This occurs due to the buildup of inflammatory fluid in the air sacs (alveoli) and nearby ducts.
According to a systematic review by Hansell et al. in 2021, lung ultrasound demonstrated a sensitivity of 92% for diagnosing consolidations. In contrast, chest X-ray only showed a sensitivity of 53% for consolidation. Studies comparing lung ultrasound (LUS) to other tools such as CT scans, chest X-rays (CXR), and lung auscultation indicate that LUS is highly accurate in detecting lung and pleural conditions. It is considered a promising alternative for bedside respiratory assessments due to its non-invasive nature, repeatability, accuracy, and lack of radiation exposure for patients and staff. Moreover, ultrasound equipment is readily available in critical care settings.
There is a vast differential diagnosis for lung consolidations. One approach is to divide conditions into acute versus chronic causes of consolidations. Below, we focus on the most common causes of consolidations:
Acute:
Chronic:
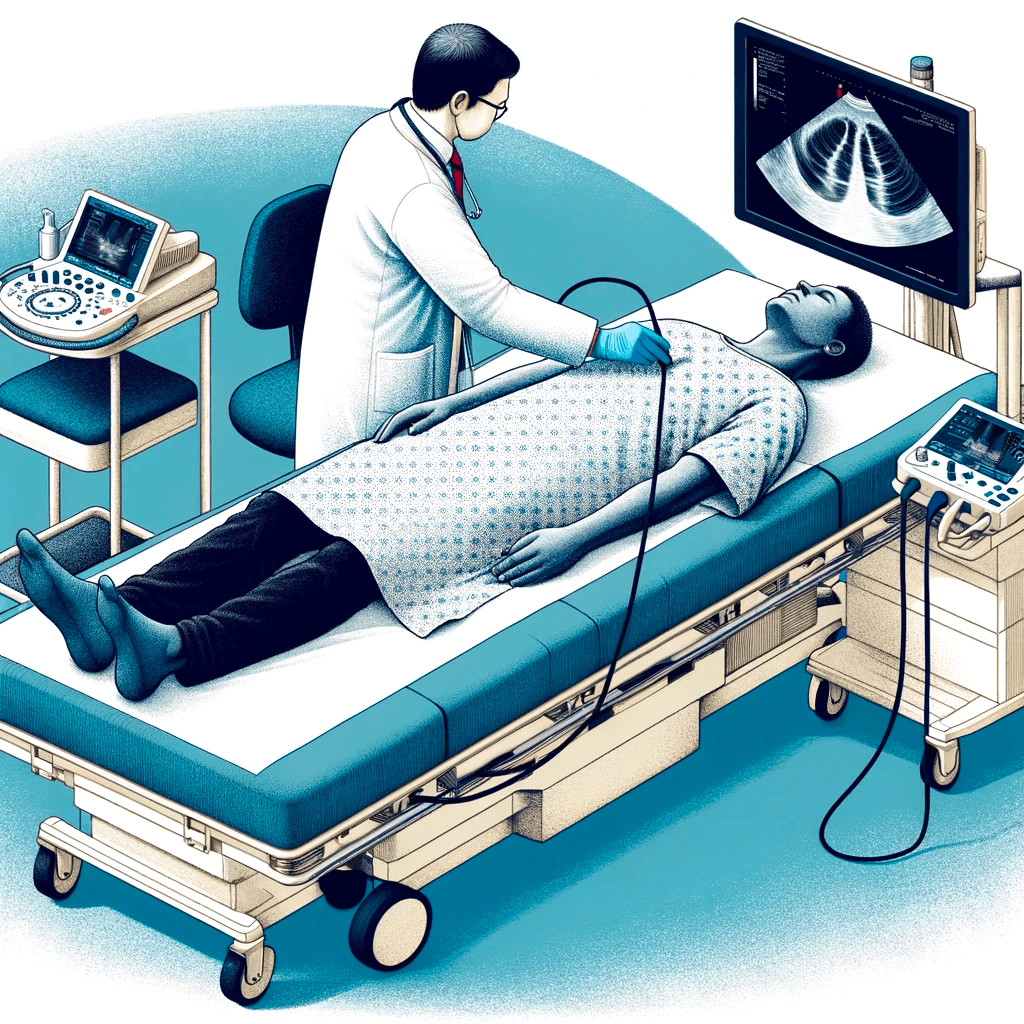
Here are some general steps that healthcare professionals may follow to detect consolidations using lung ultrasound:
Patients are most commonly assessed in a supine or semi-recumbent position, which allows for evaluation of the anterior and lateral lung fields. If the patient is able to sit upright, this will also allow for assessment of the posterior aspects of the lung.
A low frequency probe is ideal as it allows for adequate penetration into the chest and an appropriate depth. Thus, one can use either the curvilinear or phased-array probe. While the curvilinear probe has the advantage of providing an image of multiple rib spaces, the phased array probe allows the user to get in between the ribs to better visualize lung parenchyma.
Typically, a thorough lung ultrasound examines at least four lung fields: upper and lower regions on both the right and left sides. However, there are multiple protocols described in the literature to thoroughly assess the lungs. It is crucial to assess the most posterior parts of the lungs as these are where consolidations often form, particularly in critically ill patients. A limited examination may overlook smaller, more focused consolidations or other important findings.
We describe a 4 point model below to assess for consolidations. The probe marker should always be pointing toward the patient’s head.
To examine the most anterior upper lung field, position the probe on the front chest near the midclavicular line, between the 2nd and 3rd intercostal space.
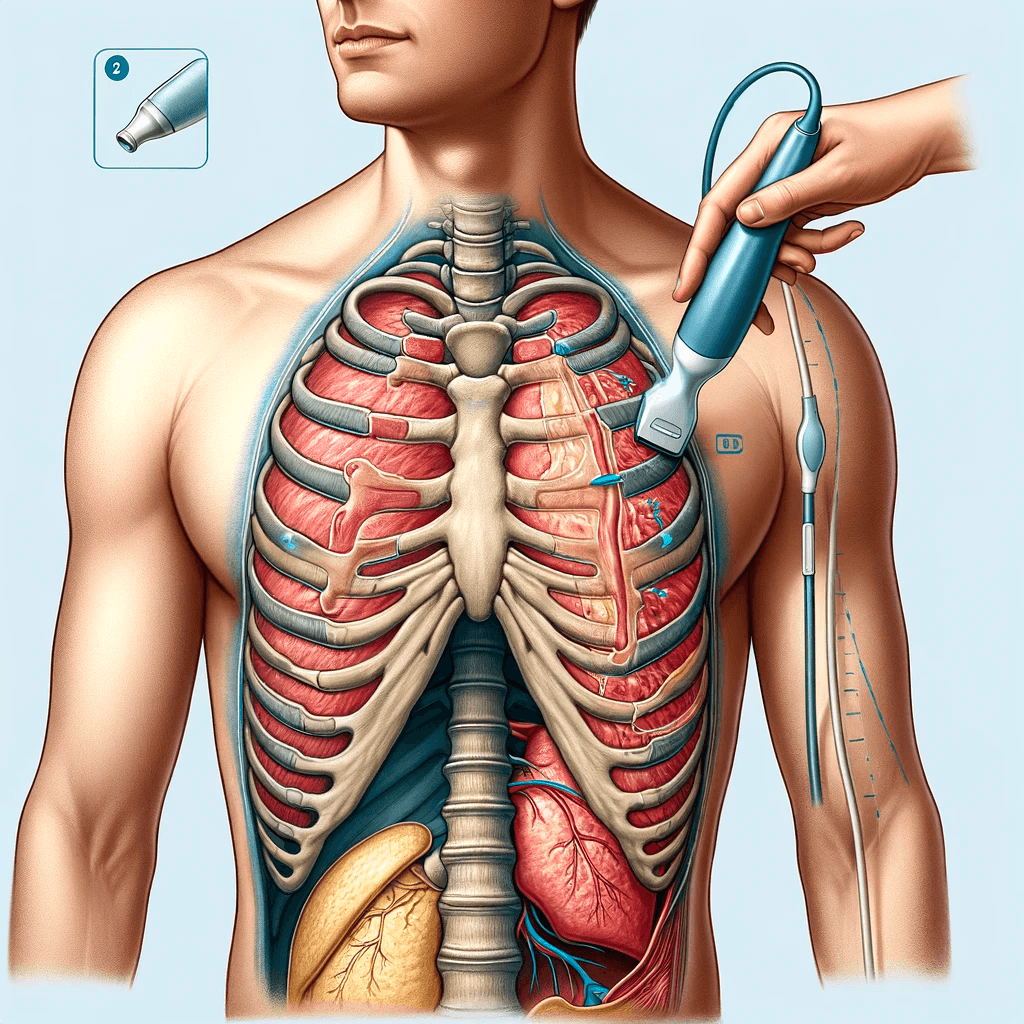
For the lateral lower lung field, place the probe at the anterior axillary line along the costophrenic angle.
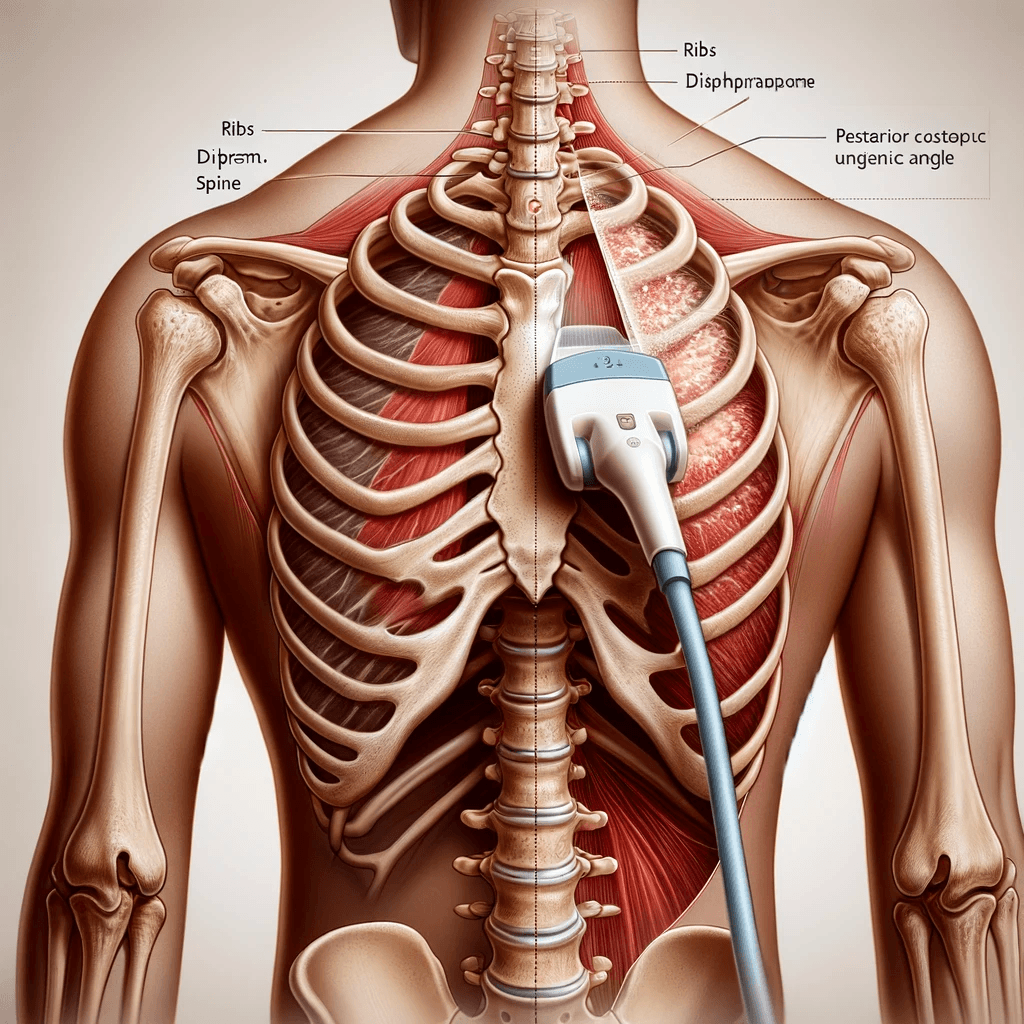
Finally, for the most posterior lung field, which is often referred to as the PLAPS point (posterior and/or lateral alveolar and/or pleural syndrome), place the probe along the costophrenic angle as close to the spine as possible. This is challenging in supine patients and thus, they may need to be repositioned.
To identify whether the lungs are normal, look for the following features:
Lung Sliding:
A Lines:
The absence of lung sliding and A lines indicates lung pathology. The next step is to search for features of lung consolidation.
Despite being caused by a variety of conditions, most lung consolidations show similar features on LUS as described below:
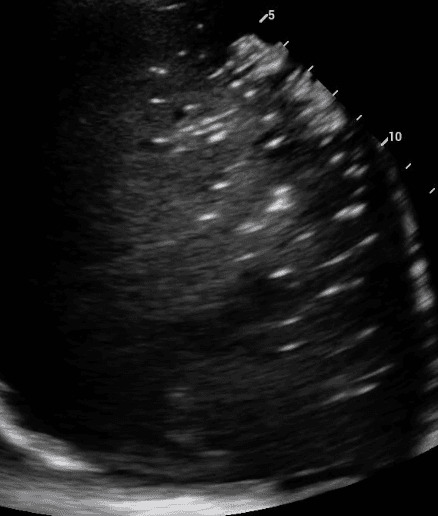
Consolidated lung appears dark due to its increased density and in some instances, may take on a similar texture to the liver. This is often referred to as “hepatization of the lung.”
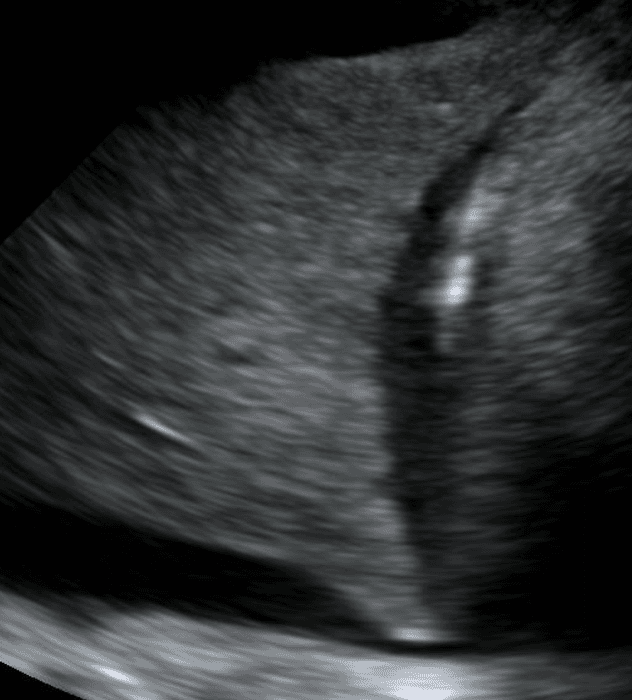
Air bronchograms are air-filled bronchi that remain patent within the surrounding consolidated lung, They appear as hyperechoic structures within the hypoechoic consolidation. They may resemble multiple millimeter-long, lentil-shaped structures or branching tubular structures.
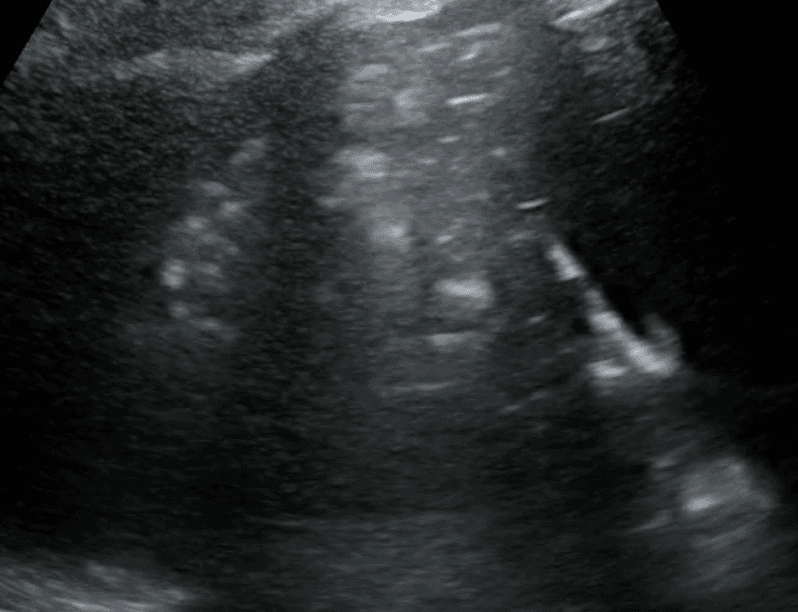
A shred sign represents the boundary between consolidated (abnormal) and aerated (normal) lung tissue. It appears as an irregular (shredded/fractal) line next to normal lung.
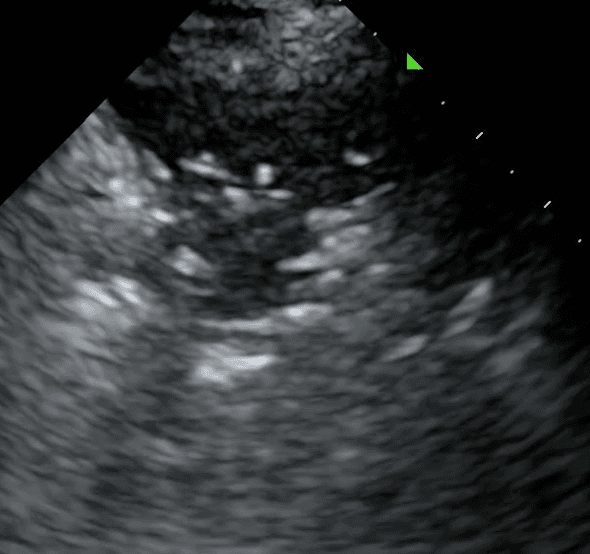
In summary, a lung consolidation is an abnormal lung that is characterized by the replacement of healthy lung tissue with substances such as pus, blood, fluid or cells. Lung ultrasound provides a rapid, non-invasive, repeatable and radiation-free method of diagnosing lung consolidations. Proper patient position, probe selection, and thorough scanning of multiple lung fields enhances diagnostic precision. Recognizing normal lung patterns and identifying the specific abnormalities outlined above are crucial.
References
Boccatonda, A., Cocco, G., D’Ardes, D., Delli Pizzi, A., Vidili, G., De Molo, C., ... & Guagnano, M. T. (2023). Infectious Pneumonia and Lung Ultrasound: A Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(4), 1402. Durant, A., & Nagdev, A. (2010). Ultrasound detection of lung hepatization. The western journal of emergency medicine, 11(4), 322–323.
Gargani, L., & Volpicelli, G. (2014). How I do it: lung ultrasound. Cardiovascular ultrasound, 12, 25.
Hansell, L., Milross, M., Delaney, A., Tian, D. H., & Ntoumenopoulos, G. (2021). Lung ultrasound has greater accuracy than conventional respiratory assessment tools for the diagnosis of pleural effusion, lung consolidation and collapse: a systematic review. Journal of physiotherapy, 67(1), 41–48.
Radiopaedia, B-line (ultrasound), accessed 19 January 2024, https://radiopaedia.org/articles/b-line-ultrasound?lang=us.
Radiology Key, Consolidation, accessed 17 January 2024, https://radiologykey.com/consolidation-4/.
Sexton, D. (2021, November 11). An Expanding Lung Mass & Assessment for Consolidations on Lung Ultrasound . January 23, 2024, https://www.thelandofem.com/blog/2021/11/11/iusotm/lung-mass
Western Sono, Lung Ultrasound Acquisition Tutorial, accessed 24 January 2024, https://westernsono.ca/screencasts/lung-ultrasound/lung-ultrasound-acquisition-tutorial-2/.
SHARE